Sintered Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnet
Sintered Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB), or “neo” magnets, is the third generation of permanent magnet developed in the 1980s. It offers the strongest magnetic power today. With its excellent magnetic characteristics Neodymium Magnet offers flexibility for new designs or is replacing older materials like Alnico and Ceramic in many applications, including high performance motors, brushless DC motors, magnetic separation, magnetic resonance imaging, sensors and loud speakers.
Why Choose Neodymium Magnet
A powder metallurgy process is used in producing sintered Neodymium magnets. Although sintered Neodymium magnet is mechanically stronger than Samarium Cobalt magnets and less brittle than other magnets, it should not be used as a structural component. Selection of Neodymium magnet is limited by temperature due to its irreversible loss and moderately high reversible temperature coefficient of Br and Hcj. The maximum application temperature is 200 °C for high coercivity grades. Neodymium magnet is more prone to oxidation than any other magnet alloys. If Neodymium magnet is to be exposed to humidity, chemically aggressive media such as acids, alkaline solutions salts and harmful gases, coating is recommended. It is not recommended in a hydrogen atmosphere.
Neodymium magnet has poor resistance to corrosion and they can also corrode from the inside-out if proper pre-treatment processes are not followed. Oftentimes, multi-layer Nickel-Copper-Nickel plating is applied to prevent failure from corrosion, but this preventative technique may not be sufficient for all applications.
Application of Neodymium Magnet
These neodymium magnets are widely used in motor, sensor, elevator, automotive, wind generator, speaker, military and aerospace industries etc.
High Temperature Stability Neodymium Magnet
With higher Hcj value, these neodymium magnet is more stable during high temperature. The tests show that the maximum permanent loss after aging is 5%.
Magneticcharacteristics and physical properties of sintered NdFeB magne
Magnetic characteristics and physical properties of sintered NdFeB magnet |
牌号 Grade | 剩磁 Br Residual Induction | 磁感矫顽力 Coercive Force | 内禀矫顽力 Intrinsic Coercive Force | 最大磁能积 (BH)max Max Energy Product | 工作温度 Working Temperature |
Br:KGs(mT) | Hcb:Koe(KA/m) | Hcj:Koe(KA/m) | (BH)max:MGOe(KJ/m3) | (TW)℃ |
N35 | 11.8-12.2(1180-1220) | ≥10.8(860) | ≥12.0(955) | 33-36(262-286) | ≤80 |
N38 | 12.2-12.6(1220-1260) | ≥10.8(860) | ≥12.0(955) | 36-39(286-310) | ≤80 |
N40 | 12.6-12.9(1260-1290) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥12.0(955) | 38-40(302-318) | ≤80 |
N42 | 12.9-13.3(1290-1330) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥12.0(955) | 40-43(318-343) | ≤80 |
N45 | 13.3-13.7(1330-1370) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥12.0(955) | 43-46(343-366) | ≤80 |
N48 | 13.7-14.0(1370-1400) | ≥10.8(860) | ≥12.0(955) | 46-49(366-390) | ≤80 |
N50 | 14.0-14.4(1400-1440) | ≥10.5(836) | ≥12.0(955) | 48-50(382-398) | ≤80 |
N52 | 14.2-14.5(1420-1450) | ≥10.5(836) | ≥12.0(955) | 50-52(398-413) | ≤80 |
N35M | 11.8-12.2(1180-1220) | ≥10.8(860) | ≥14.0(1114) | 33-36(262-286) | ≤100 |
N38M | 12.2-12.6(1220-1260) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥14.0(1114) | 36-39(286-310) | ≤100 |
N40M | 12.6-12.9(1260-1290) | ≥11.4(910) | ≥14.0(1114) | 38-40(302-318) | ≤100 |
N42M | 12.9-13.3(1290-1330) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥14.0(1114) | 40-43(318-343) | ≤100 |
N45M | 13.3-13.7(1330-1370) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥14.0(1114) | 43-46(343-366) | ≤100 |
N48M | 13.7-14.0(1370-1400) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥14.0(1114) | 46-49(366-390) | ≤100 |
N50M | 14.0-14.4(1400-1440) | ≥11.5(915) | ≥14.0(1114) | 48-50(382-398) | ≤100 |
N35H | 11.8-12.2(1180-1220) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥17.0(1353) | 33-36(262-286) | ≤120 |
N38H | 12.2-12.6(1220-1260) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥17.0(1353) | 36-39(286-310) | ≤120 |
N40H | 12.6-12.9(1260-1290) | ≥11.5(915) | ≥17.0(1353) | 38-40(302-318) | ≤120 |
N42H | 12.9-13.3(1290-1330) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥17.0(1353) | 40-43(318-343) | ≤120 |
N45H | 13.3-13.7(1330-1370) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥17.0(1353) | 43-46(343-366) | ≤120 |
N48H | 13.7-14.0(1370-1400) | ≥12.2(938) | ≥17.0(1353) | 46-49(366-390) | ≤120 |
N35SH | 11.8-12.2(1180-1220) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥20.0(1593) | 33-36(262-286) | ≤150 |
N38SH | 12.2-12.6(1220-1260) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥20.0(1593) | 36-39(286-310) | ≤150 |
N40SH | 12.6-12.9(1260-1290) | ≥11.5(915) | ≥20.0(1593) | 38-40(302-318) | ≤150 |
N42SH | 12.9-13.3(1290-1330) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥20.0(1593) | 40-43(318-343) | ≤150 |
N45SH | 13.3-13.7(1330-1370) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥20.0(1593) | 43-46(343-366) | ≤150 |
N30UH | 10.8-11.4(1080-1140) | ≥10.1(804) | ≥25.0(1990) | 28-31(223-246) | ≤180 |
N33UH | 11.3-11.7(1130-1170) | ≥10.3(820) | ≥25.0(1990) | 30-33(239-262) | ≤180 |
N35UH | 11.8-12.2(1180-1220) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥25.0(1990) | 33-36(262-286) | ≤180 |
N38UH | 12.2-12.6(1220-1260) | ≥11.2(892) | ≥25.0(1990) | 36-39(286-310) | ≤180 |
N40UH | 12.6-12.9(1260-1290) | ≥11.5(915) | ≥25.0(1990) | 38-40(302-318) | ≤180 |
N42UH | 12.9-13.3(1290-1330) | ≥11.8(938) | ≥25.0(1990) | 40-43(318-343) | ≤180 |
N30EH | 10.8-11.4(1080-1140) | ≥10.1(804) | ≥30.0(2388) | 28-31(223-246) | ≤200 |
N33EH | 11.3-11.7(1130-1170) | ≥10.3(820) | ≥30.0(2388) | 30-33(239-262) | ≤200 |
N35EH | 11.8-12.2(1180-1220) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥30.0(2388) | 33-36(262-286) | ≤200 |
N38EH | 12.2-12.6(1220-1260) | ≥11.2(892) | ≥30.0(2388) | 36-39(286-310) | ≤200 |
N30AH | 10.8-11.4(1080-1140) | ≥10.1(804) | ≥35.0(2785) | 28-31(223-246) | ≤220 |
N33AH | 11.3-11.7(1130-1170) | ≥10.3(820) | ≥35.0(2785) | 30-33(239-262) | ≤220 |
N35AH | 11.8-12.2(1180-1220) | ≥11.0(876) | ≥35.0(2785) | 33-36(262-286) | ≤220 |
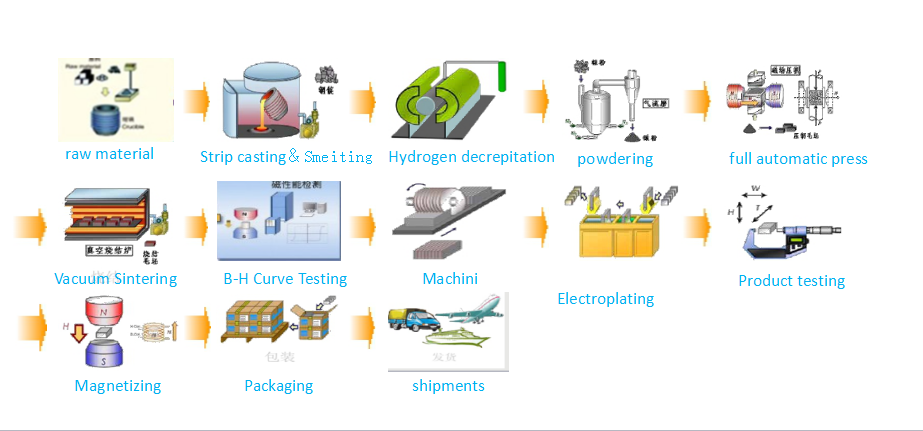
Manufacturing process
Sintered Nd-magnets are manufactured by a powder metallurgical process. The raw materials, Fe, Nd, B etc.are melted in a furnace and then cast into thin sheet by strip casting. The material is pulverized firstly by hydrogen decrepitation and then by jet milling under protetctive atmosphere. The powder is then oriented with external magnetic field and pressed into blocks or near net shape. Final properties and density are achivied in following sintering and heat treatments. The blocks are then cut to shape, surface treated against corrosion and magnetized.
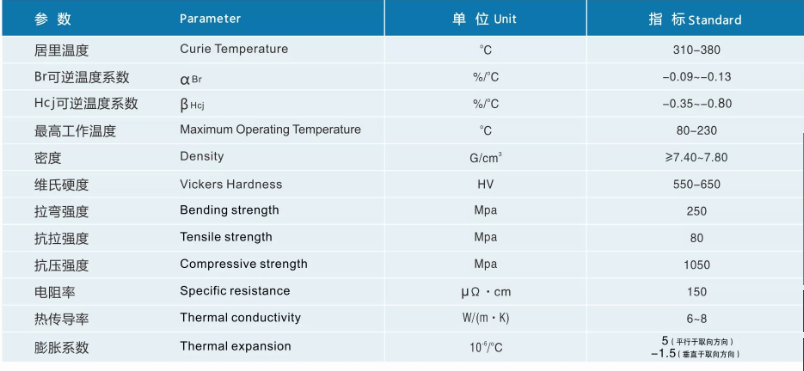
Physical properties
The typical physical properties of NdFeB are given in the table below.These values must not be understood as guaranteed, as the properties are not controlled in manufacture. NdFeB magnets are fragile and must never be used as load carrying elements in a design. Please note that the coefficient of thermal expansion is positive along the magnetizing axel and negative perpendicular to the magnetization.