Ferrite Magnets
Item specifics
- Material
- Sintered Ferrite Magnets
- Shape
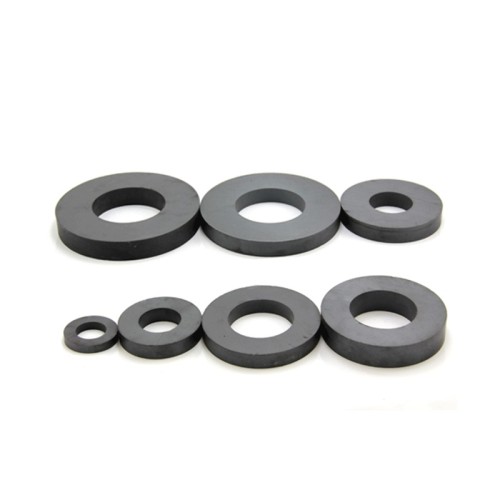
- Main Disc, but Block or Rectangular or Cuboid, Ring, Cylinder, Arc and Irregular shape are also available
- Magnetized direction
- Axially or Diametrical Magnetized, but Thickness, Multipoles and Radial magnetization are also available
- Certificate
- ISO/TS 16949, ISO9001, ISO14001, RoHS, REACH
- Packing
- Standard sea or air packing, such as carton, wooden box, pallet etc.
- Transportation
- courier (TNT, DHL, FedEx, UPS), air or sea.
Review
Description
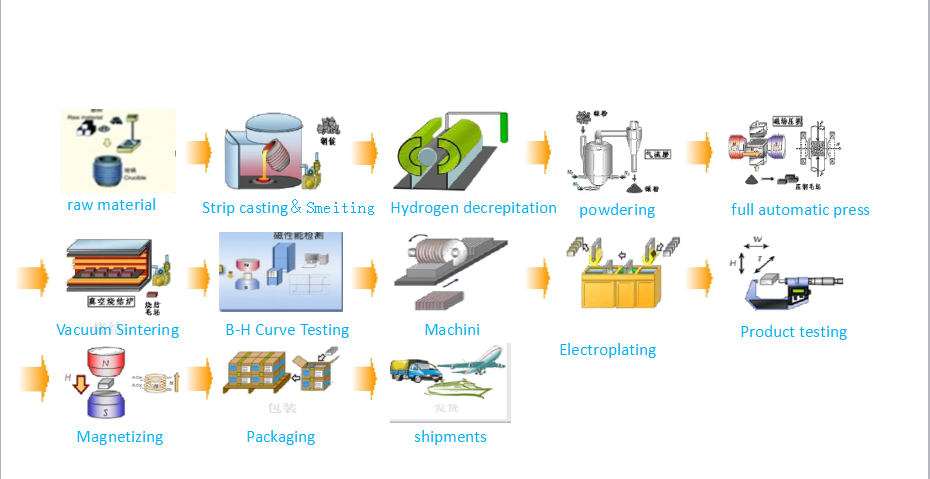
Since the 1950s, hard ferrite (ceramic) magnets have been widely applied because of low cost, good magnetic properties and excellent environmental stability. Both isotropic and anisotropic hard ferrite magnets are available for Cinfer. The magnetic energy products of anisotropic hard ferrite magnets are higher than that of the isotropic hard ferrite magents by up to 300%. Depending on the base materials, there are Barium Ferrite and Strontium Ferrite with higher coercive. After preliminary inspection, the raw materials (mainly iron oxide, strontium carbonate) are weighed, blended, pre-sintered and milled to fine powders with hexagonal crystals. For isotropic magnets, the pre-materials are milled to powders and then pressed. For anisotropic magnets there are two procedures in the production, dry press and wet press. Firstly, the raw materials are dried and then pressed in a magnetic field. Secondly, the raw materials are wet pressed under the influence of a magnetic field, then followed by sintering, finishing cleaning and magnetization. Finally the surface can be machined, marked, magnetized or coated according to customers' requirements.
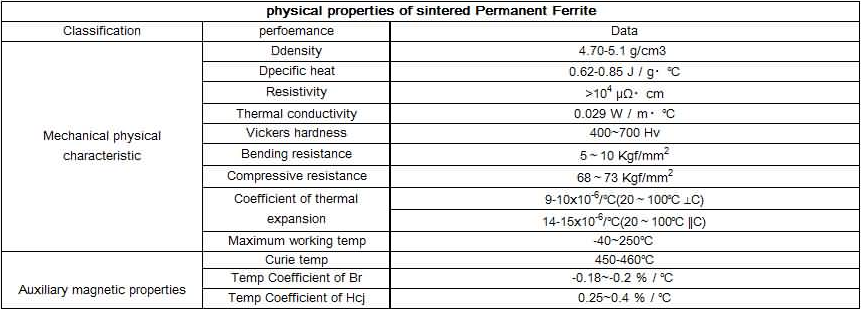
Ceramic magnets are very hard and brittle, consequently machining must be done with a diamond wheel, and is easier when done prior to magnetization. Standard tolerances for ceramic magnet dimensions are +/-.005″ for ground dimensions and +/- 2% of feature size for dimensions. Because of their brittleness these magnets will not withstand impact or flexing. We recommend that they not be used for structural purposes.Ceramic magnets are chemically inert non-conductors, which is a benefit in many applications according to different grade as below
Maximum operating temperature for a ceramic magnet is 250°C. Although you will experience magnetic losses when operating at elevated temperatures, the losses are recovered when the material is brought down to normal ambient temperature. However, operating in very cold temperatures (-20°C) can result in permanent losses of magnetic strength unless the circuit has been designed for such extremes.
Pros:
1. least expensive material compared to alnico magnets or rare earth magnets
2. High intrinsic coercive force
3. Corrosion resistance